MSU biochemist receives $2.8 million NIH grant for epigenetic research on autism spectrum disorder
EAST LANSING, Mich.— As a developmental and neurological condition, autism spectrum disorder (ASD) manifests in a variety of ways, including difficulty communicating, limited or repetitive behavior, and even a higher risk of seizures. But what if the study of a single gene could revolutionize our understanding of ASD’s complexities and lead the way to better therapeutic care?

Such questions are at the heart of research being done by Michigan State University biochemist Jin He, who recently received a five year, $2.8 million R01 grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). He, an assistant professor who joined the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (BMB) in 2015, received NIH funding to continue his investigation into the role of the ASH1L (Absent, Small, or Hometoic discs 1-Like) gene in the origins of ASD, and specifically, the impact of epigenetics—non-genetic processes that regulate gene expression.
ASH1L typically plays a role in gene expression by encoding a protein known as histone methyltransferase and is crucial in regulating gene expression in normal development. While recent studies have identified ASH1L as one of the highest risk genes associated with ASD, little is known about the exact mechanisms underlying ASH1L’s function in the development of autistic-like symptoms.
To date, He and his team have made significant discoveries by using innovative models that “knock out” the ASH1L gene in the brains of mice. Without ASH1L, mice displayed telltale signs of ASD including behavior and memory deficits. Furthermore, when administered a histone deacetylase inhibitor postnatally, autistic-like deficits were seen to be lessened in young mice, raising exciting possibilities for therapeutics and a future human cure.
“In the US alone, 2.6% of children younger than eight years old have ASD, and more than 5 million adults live with it as well,” He said. “When we published some of our first results we received many emails from families impacted by ASD, and we could sense the devastating challenges they faced. Currently, therapy is only targeted at symptoms. I hope that through our studies—based on biological mechanisms—we can provide new therapeutic possibilities. This is what’s most exciting for me.”
The latest funding from the NIH will support an examination of the particular brain and molecular mechanisms at play in relation to ASH1L and ASD. In previous mice studies, a loss of ASH1L was seen to spur neural hyperactivity, and an excitation/inhibition (E/I) imbalance in the brain. To better understand these imbalances, He and his team will study three lineages of mice in which ASH1L has been deleted in particular neuron types: cortical excitatory neurons, cortical inhibitory neurons, and astrocytes.
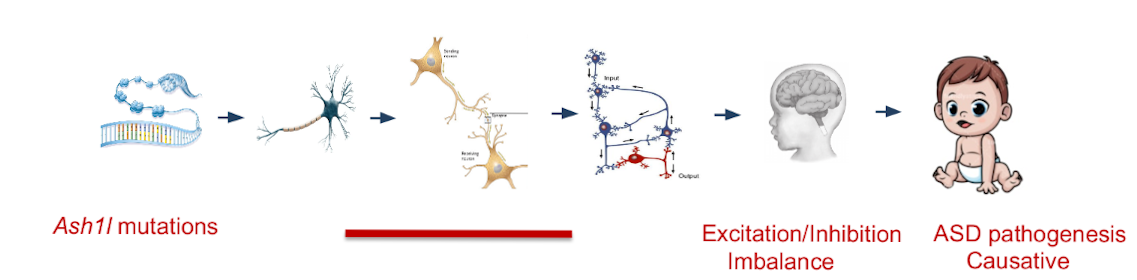
This top-down approach, He explained, is one of the first steps in developing therapeutic measures: “We’re trying to pinpoint where, when, and what kind of changes are occurring. If we can define the gene, define the neuron type, and define the stage of development, this will provide very precise information when it comes to intervening gene therapy.”
He’s research will continue a generative and longstanding collaboration with MSU colleagues in BMB and beyond, including co-investigators Alfred Robison (Physiology) and George Mias (BMB).



